
Meniere’s disease is a disorder that causes sudden attacks of vertigo, a sensation that you or your surroundings are moving or spinning; nausea; cold sweat; or vomiting.
Meniere’s disease is slightly more common in females than males, and majority of the patients have an onset at their late 30’s to late 50’s. Many sufferers suspect that they have Meniere’s disease when they experience a dizziness or vertigo. However, only 10% of these sufferers are diagnosed with Meniere’s disease while 90% of them are not. In fact, Meniere’s disease is a disease which causes very severe and painful symptoms and can be confused with other illness.
In this article, a neurologist Dr. Yoshiya Hasegawa, will give you an insight into the difference between severe dizziness and Meniere’s disease.
Contents
1. Common causes and symptoms of Meniere’s disease
Meniere’s disease is considered to be related to an excessive build-up of endolymph fluid in semicircular canals and the cochlea which are located in the inner ears. Semicircular canals and otolithic apparatus are responsible for a sense of balance and equilibrium while cochlea for hearing, and they are filled with the endolymph fluid. An excessive build-up of the endolymph fluid interferes with the function of semicircular canals and it causes dizziness. It also has an effect against cochlea and leads to hearing loss or tinnitus (a ringing in one’s ears.)
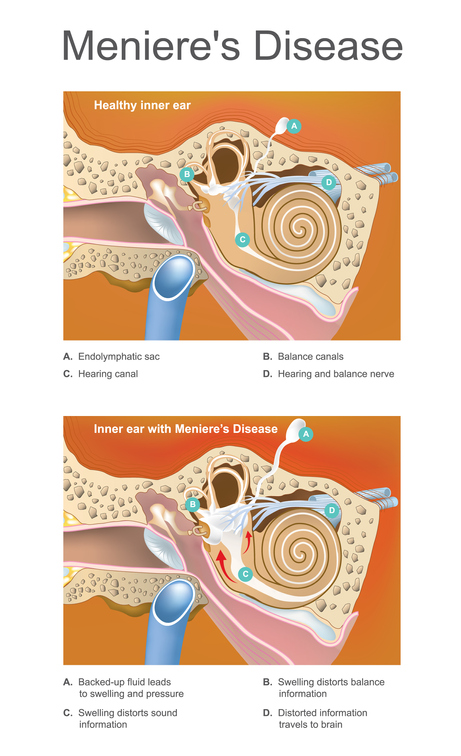
Disorder of the inner ear that can effect hearing and balance to a varying degree.
One of the possible causes of Meniere’s disease, an excess fluid, can trigger a triad of symptoms consisting of vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus.
2. Three critical points for Meniere’s disease
There are three facts which sufferers should know.
2-1. Diagnosis of Meniere’s disease should be based on a combination of the set of symptoms
If you suffer from only dizziness, chances of having Meniere’s disease may be lower. The key factor in diagnosing Meniere’s disease is “recurrent episodes” of its symptoms, which requires sufficient examinations including medical interviews. Physical examinations including nystagmus and hearing test will be administered to observe one’s balance and hearing ability.
2-2. Non-specialists might be unfamiliar with diagnosing dizziness
In my opinion, there seem to be many doctors who are not familiar with diagnosing dizziness. Patients with dizziness may become more nervous about their symptoms if they are unable to get correct diagnosis/treatment or clear explanation about their conditions. Many patients often end up getting diagnosed with “Meniere’s disease” when they visit non-specialists. However, this diagnosis may be incorrect if doctors are unfamiliar with “Meniere’s disease.”
When you are asked by the doctor about having experienced any symptoms such as tinnitus, feeling of fullness in the ear (aural fullness), or reducing hearing (hearing loss), your doctor shows a deeper understanding of dizziness. Remember that there are some doctors who fail to ask this critical question which helps lead to a more accurate diagnosis.
You should visit ENT or neurology specialists to avoid being misdiagnosed when you have dizziness.
2-3. Meniere’s disease consists of hearing impairments
Meniere’s disease usually presents with “recurring vertigo episodes consisting of hearing impairments such as hearing loss, tinnitus and aural fullness”. The critical factor in diagnosing Meniere’s disease is whether it “consists of hearing impairments.” If you are diagnosed with “Meniere’s disease” when you only have dizziness without having experienced any hearing impairments (hearing loss, tinnitus and aural fullness), you may wish to seek a second opinion.
3. Possible diseases other than Meniere’s disease
If your dizziness does not accompany any hearing impairments (hearing loss, tinnitus or aural fullness), there may be other diseases/causes than Meniere’s disease.
3-1. Stiff shoulders
I frequently find that many outpatients with stiff shoulders suffer from dizziness. They tend to be busy, sleep-deprived, fatigued or lacking in exercises which often leads to a higher physical/psychological tension. This type of physical condition may cause chronic lightheadedness or dizziness and medical examinations will not show any particular cause. In such cases, doctors need to explain that sufferers are “not sick” and try to alleviate their anxiety, encourage them to get rest and do some exercises. This will usually help improve their symptoms.
3-2. Dizziness triggered by a deformed cervical spine
There are four blood vessels running towards the brain, and two vessels in the back of the neck are called vertebral arteries which proceed superiorly in the transverse foramen of each cervical vertebra. These vessels tend to be compressed when you move your neck and may lead to dizziness. Situations in which dizziness is more likely to occur seems to be associated with neck movement such as: upon waking; when you wake up to visit the bathroom at night; or when you look down or look back; or a deformed cervical spine.
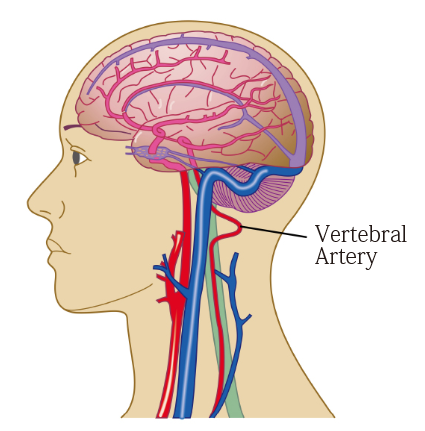
Vertebral Artery
Poor circulation of the vertebral artery in cervical vertebra may cause dizziness.
3-3. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo causes vertigo which lasts 30 seconds to one minute when you get in and out of bed. It does not accompany hearing loss, tinnitus or other nerve-related symptoms such as numbness in the limbs. Some people may feel lightheadedness when they tip their head back or look back. The reclining position of your head when your hair is being shampooed over the sink at a hair salon or when you are being examined by a dentist may also trigger this type of vertigo.
You might be suspected of BPPV if you feel dizzy when you change your head position.
4. Diagnostics
There are one-leg standing test, Mann test, or stepping test to demonstrate the degree of equilibrium disturbance, and hearing test, nystagmus test, or drug infusion test to observe the presence of hearing impairments.
4-1. Balancing test
A test is administered in determining the degree of equilibrium disturbance by standing still with one’s eyes closed. Patients will experience difficulty to stand steady if they have Meniere’s disease. Testing methods include a one-legged stance test, and a Mann’s test which examines body equilibrium in a standing position with one foot placed in front of other at the midline applying equal weight on each leg. A stepping test is also used to determine Meniere’s disease, and patients are asked to march for 30 seconds in place with eyes closed. They may be unable to maintain position and will turn toward the affected side when they have Meniere’s disease.
4-2. Hearing test
A hearing test is administered as well in order to determine Meniere’s disease. It is a popular assessment where patients are asked to push a button when they hear sounds like high pitch or low pitch tones. Doctors might snap their fingers right behind the patient’s ears to test if they have lost their hearing. Some patients do not notice that they have lost their hearing. You can try this self-check test by finger snapping to evaluate your hearing ability when you feel dizzy.
A popular “hearing test” is used to determine the presence of Meniere’s disease.
4-3. Drug infusion testing
Drug infusion testing is when medicine is given to see how the body reacts to the drugs. Glyceol which has a diuretic effect works effectively against endolymphatic hydrops caused by Meniere’s disease and improves hearing ability drastically.
5. Treatments
There are some commonly used treatments for Meniere’s disease.
5-1. Diuretics
Diuretics are used for treatment of Meniere’s disease. Diuretics are believed to increase metabolism of water and help in reducing endolymphatic hydrops. Glyceol infusion mentioned earlier is often administered. Isobide, which is an oral medicine with a diuretic effect, may not be recommended due to its unpleasant taste.
5-2. Sodium hydrogen carbonate infusion (Sodium bicarbonate intravenous infusion)
A medicine called Meylon is administered by intravenous infusion which is “sodium bicarbonate” containing sodium hydrogen carbonate as an active ingredient, and it works effectively against nausea and dizziness by increasing the PH level of blood. It is commonly used for acute or attack episodes. If the condition is severe, patients may need to be hospitalized and receive infusion therapy.
5-3. Antiemetic
Patients suffering from dizziness with nausea and vomiting will be administered with an antiemetic drug as well. In cases where they are unable to take oral medication, an antiemetic drug is added to glyceol or meylon infusion.
5-4. Anti-anxiety agent
Some symptoms are more likely to be relieved by adding anti-anxiety agent since stress and anxiety is believed to be strongly linked to Meniere’s disease. Intramuscular injection with an anti-anxiety agent such as Diazepam is administered to acute dizziness sufferers with severe anxiety. Anti-anxiety agent may help reduce dizziness by facilitating the initial stage of vestibular compensation mechanism, a function of the brain which controls body balance and equilibrium when one feels dizzy.
Infusion is one of the effective treatment methods when patients suffer from nausea.
6. Other non-medical treatments
It is believed that stress may lead to Meniere’s disease. Therefore, do not strain yourself too much. Plenty of sleep, regular exercise and engagement in hobbies are important to prevent overwork.
6-1. Diets
Diets are deeply related to all of physical conditions such as nerves and muscles. Orderly eating can lead to wellness at each stage of the human life cycle. Psychological stability has a great effect especially against ears. Try to eat a well-balanced diet because research suggests that it affects not only our physical health, but mentally and emotionally, too. Also, it can help to improve inner ear blood flow.
6-2. Sleep
Plenty of sleep is necessary to enjoy good mental health and deal with stress. Sleep deprivation causes poor balance of autonomic nervous system, which consists of a sympathetic nerve and a parasympathetic nerve. Therefore, you should get quality sleep, that is one of the best things you can do for your physical and psychological health.
6-3. Exercise
You do not need a hard workout; walking, stretching, and light jogging will be sufficient. Light exercise will help increase your metabolism and improve blood flow, which has a positive effect on your inner ears.
6-4. Avoid cigarette and alcohol
Nicotine contained in a cigarette causes poor circulation of blood. It leads to an increase of Reactive Oxygen Species, which has an adverse effect against both outer and inner body. Therefore, smoking habit should be discontinued. Moderate consumption of alcohol may have a positive influence. However, alcohol dehydrates the body and leads to other illnesses if you consume too much. Also, it has an adverse effect against your ears. Hence, you should control your alcohol intake.
7. Summary
- If you are diagnosed with Meniere’s disease without the presence of hearing impairments (hearing loss, tinnitus and aural fullness), you may wish to seek a second opinion.
- Dizziness without hearing impairments (hearing loss, tinnitus and aural fullness) is less likely to be a symptom of Meniere’s disease.
- You should visit ENT or neurology specialists when you experience dizziness.

